Toronto’s population is highly educated and diverse. The education sector is one of the city’s largest employers, with 1,400 educational establishments and related businesses and more than 100,000 employees. Total annual wages for the sector are $7.2B.
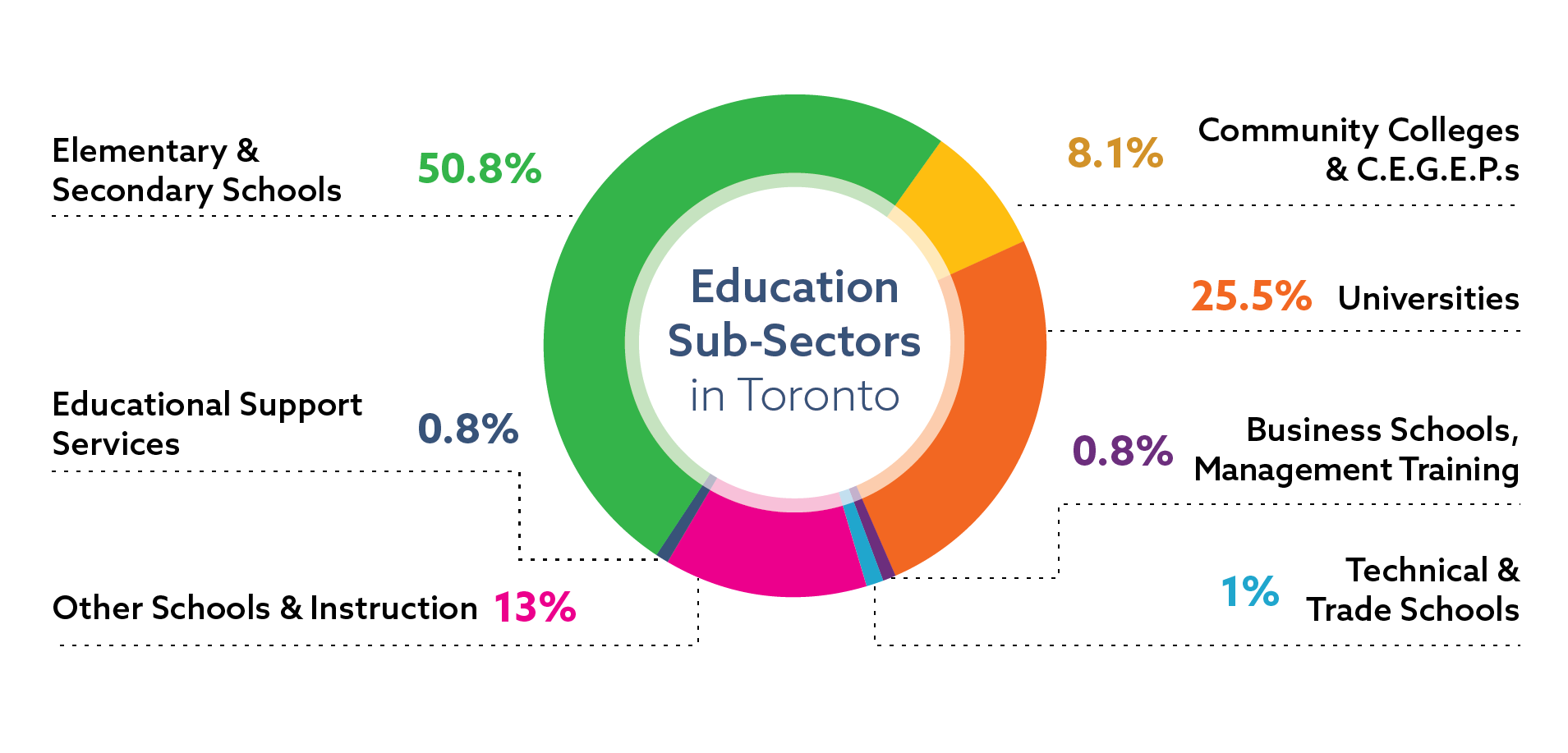
Distribution of Jobs in the Education Sector
- Elementary & secondary schools – 50.8%
- Universities – 25.5%
- Other schools & instruction – 13%
- Community colleges – 8.1%
- Business schools & management training – 0.8%
- Educational support services – 0.8%
[Sector data is derived from a number of sources including the Labour Force Survey, 2006 Census, 2011 National Household Survey, Canadian Business Counts, and the City of Toronto’s Employment Survey. The methodology used to identify clusters and their sizes is based on methodology used by the Institute for Competitiveness and Prosperity in its 2017 Cluster Study.]
Key Sector Assets - Universities & Colleges
Universities
Toronto is home to six publicly-funded universities and four private university with over 205,000 students (Full-Time and Part-Time, 2021-22) enrolled in various programs
Public:
- OCAD University
Founded in 1876, OCAD U is dedicated to art and design education, and its programs and research bridge fields of digital media and design, sustainability, health and wellness, cultural diversity and indigenous cultures.
- Toronto Metropolitan University
Toronto Metropolitan University offers 62 bachelor’s programs and 55 PhD and master’s programs, and its DMZ incubator is ranked one of the top university incubators in North America.
- Université de l’Ontario français (UOF)
Founded in 2021, this is the sole French-language public university in the province of Ontario. Initially academic programs are divided in four bachelor’s degree programs and several microprograms.
- University of Toronto
Founded in 1827, the University of Toronto is Canada’s leading institution of learning, discovery and knowledge creation, and is one of the world’s top research-intensive universities. The university offers a wide range of undergraduate and graduate degree programs and is home to several professional schools.
- York University
York University is one of the leading interdisciplinary research and teaching institutions in Canada, offering more than 200 undergraduate and graduate degree programs on its two campuses in Toronto.
- University of Guelph-Humber
The University of Guelph-Humber (a collaboration between the University of Guelph and Humber College Institute of Technology & Advanced Learning) was the first in Ontario to offer an opportunity to earn both a university honours degree and diploma in four years of full-time study in one location when UofGH opened its doors in 2002.
Private:
- Northeastern University Toronto
This regional campus of the U.S.-based university offers Master of Science programs in project management, information assurance and cyber security, and regulatory affairs for drugs, biologics and medical devices.
Colleges
Toronto is home to five publicly-funded community colleges with over 88,000 students (Full-Time, 2021-22) enrolled in various programs:
-
- Centennial College
Ontario’s first community college, Centennial College offers industry-recognized full- and part-time programs at four Toronto campuses, and has a presence in countries like China, India, South Korea and Brazil.
- George Brown College
Focusing on applied arts and technology, George Brown College offers a range of degree, diploma, certificate and apprenticeship training programs at three campuses.
- Humber College
Humber emphasizes hands-on, career-focused learning, and offers a broad range of credentials including bachelor’s degrees, diplomas, certificates and postgraduate certificates.
- Seneca College
With campuses throughout the Greater Toronto Area, Seneca College offers opportunities for hands-on learning in programs related to applied arts, business, financial services and technology.
- Collège Boréal in Toronto
A new campus of Collège Boréal was officially inaugurated in Toronto’s Distillery Historic District. It is a key hub for French-language post-secondary education, employability, immigration, and business.
Key Sector Assets - Elementary and Secondary Schools
- Toronto District School Board
The Toronto District School Board is the largest and one of the most diverse school boards in Canada. The TDSB serves approximately 246,000 students in 583 schools throughout Toronto, and more than 140,000 life-long learners in its Adult and Continuing Education programs.
- Toronto Catholic District School Board
The Toronto Catholic District School Board provides publicly-funded Catholic education to more than 91,000 students in its 195 schools.
- Conseil scolaire Viamonde and Conseil scolaire de district catholique Centre-Sud
French-language public education is offered by two smaller school boards that operate in Toronto.
- Private schools
In addition to publicly-funded educational institutions, Toronto has many private schools that offer elementary and secondary school programs.
Key Sector Assets - Private Career Colleges
- Toronto has more than 200 private career colleges that offer certificate and diploma programs in fields such as business, health services, human resources, applied arts, information technology, electronics, trades and services.
- The Government of Ontario requires that private career colleges be registered and offer provincially-approved programs, and maintains a searchable directory of approved colleges and programs.
Key Sector Assets - Language Schools
- There are about 40 language training schools and programs in Toronto, both private and publicly-funded. The majority of these schools provide English- and some French-language education targeted mostly to foreign students and professionals.

